
powerSpectrum = ABS(ffTransform)^ 2 scaledPowerSpect = ALOG10(powerSpectrum) Display the log-scaled power spectrum as an image. ffTransform = FFT(binary_img, /CENTER) Compute the power spectrum of the transform and apply a log scale. binary_img = READ_BINARY(file, DATA_DIMS = imageSize) Display the original image img01 = image(binary_img, RGB_TABLE = 6) Transform the image into the frequency domain and shift the zero-frequency location from (0,0) to the center of the data. imageSize = file = FILEPATH( 'm51.dat', $ SUBDIRECTORY = ) Use READ_BINARY to read the image as a binary file. Power spectrum image (left) and surface plot (right). The red background pixels have been reduced in the second image. Below is the original image of M-51 galaxy (left) and inverse-FFT-transformed image (right). The code shown below creates the following images, each displayed in separate windows. The example data is available in the examples/data directory of your IDL installation. See Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) Background for a more complete description of this process. Perform an inverse FFT to transform the image back to the spatial domain.Apply a mask to the FFT-transformed image.Compute a power spectrum and determine threshold to filter out noise.
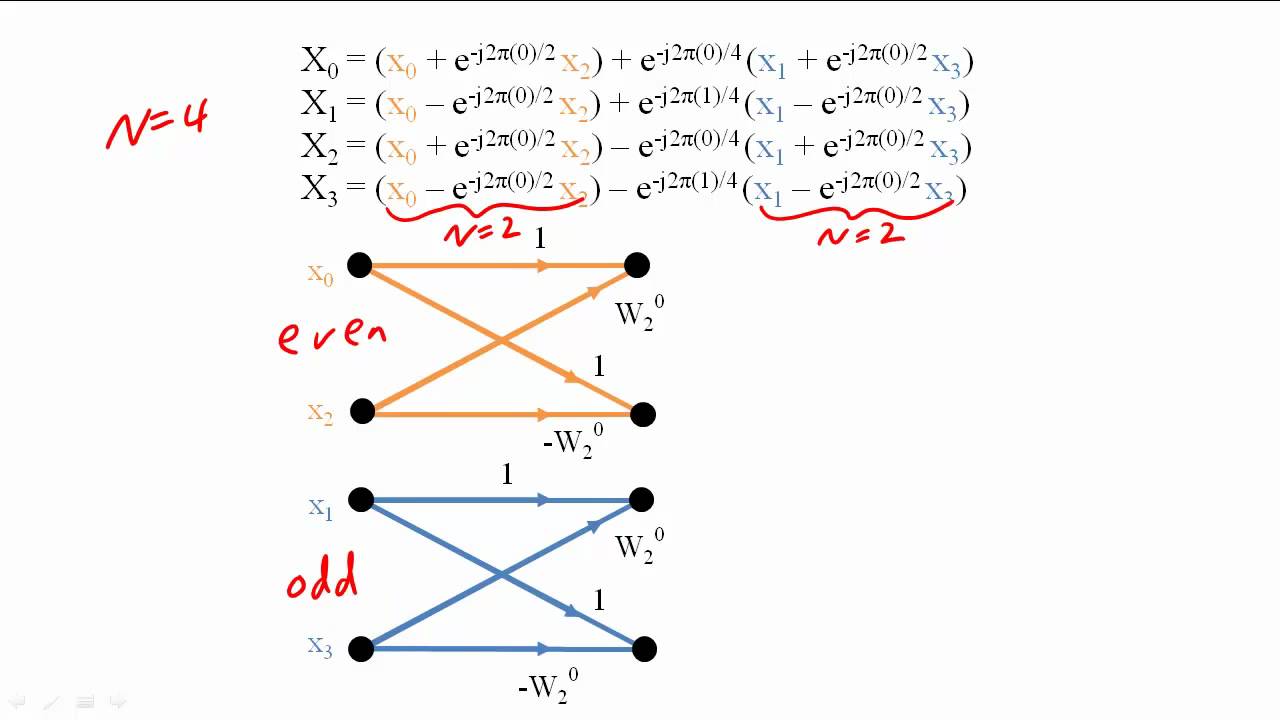
Perform a forward FFT to transform the image to the frequency domain.The following example shows how to remove background noise from an image of the M-51 whirlpool galaxy, using the following steps: The Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is used to transform an image from the spatial domain to the frequency domain, most commonly to reduce background noise from the image.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
